本讲是android camera专题系列的第41讲,我们介绍android camera2 api专题的touch ae实战。
更多资源:
| 资源 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 在线课程 | |
| 知识星球 | 星球名称:深入浅出android camera 星球id: 17296815 |
| 极客笔记圈 |
判断是否支持设置ae regions
cameracharacteristics.control_max_regions_ae
private void printmaxaeregions(context context, int cameraid) {
try {
string cameraids = mcameramanager.getcameraidlist()[cameraid];
cameracharacteristics characteristics = mcameramanager.getcameracharacteristics(cameraids);
integer regioncount = characteristics.get(cameracharacteristics.control_max_regions_ae);
log.i(tag, "[touch aeaf]cameraid:" cameraids ", printmaxaeregions:" regioncount);
} catch (exception e) {
}
}
点击屏幕设置touch ae(坐标系转换)
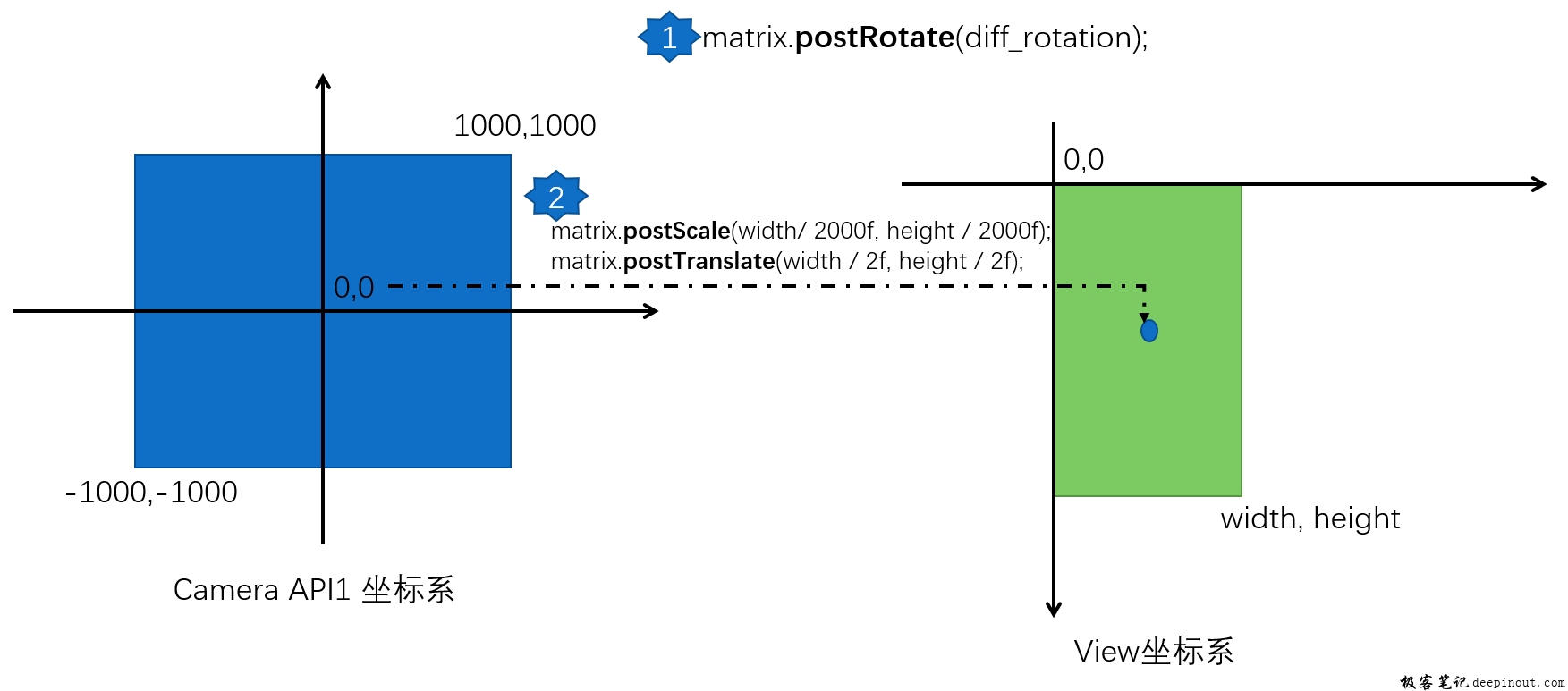
camera坐标系转换到view坐标系
private void calculatecameratopreviewmatrix() {
if( mydebug.log )
log.d(tag, "calculatecameratopreviewmatrix");
if( mcameracontroller == null )
return;
camera_to_preview_matrix.reset();
if( !using_android_l ) {
// see http://developer.android.com/reference/android/hardware/camera.face.html#rect
// need mirror for front camera
boolean mirror = (mcameracontroller.getfacing() == cameracontroller.facing.facing_front);
camera_to_preview_matrix.setscale(mirror ? -1 : 1, 1);
int display_orientation = mcameracontroller.getdisplayorientation();
if( mydebug.log ) {
log.d(tag, "orientation of display relative to camera orientaton: " display_orientation);
}
camera_to_preview_matrix.postrotate(display_orientation);
}
else {
// unfortunately the transformation for android l api isn't documented, but this seems to work for nexus 6.
// this is the equivalent code for android.hardware.camera.setdisplayorientation, but we don't actually use setdisplayorientation()
// for cameracontroller2, except testing on nexus 6 shows that we shouldn't change "result" for front facing camera.
boolean mirror = (mcameracontroller.getfacing() == cameracontroller.facing.facing_front);
camera_to_preview_matrix.setscale(1, mirror ? -1 : 1);
int degrees = getdisplayrotationdegrees();
log.d(tag, "[touch aeaf] view degrees:" degrees);
int result = (mcameracontroller.getcameraorientation() - degrees 360) % 360;
if( mydebug.log ) {
log.d(tag, "orientation of display relative to natural orientaton: " degrees);
log.d(tag, "orientation of display relative to camera orientaton: " result);
}
camera_to_preview_matrix.postrotate(result);
}
// camera driver coordinates range from (-1000, -1000) to (1000, 1000).
// ui coordinates range from (0, 0) to (width, height).
camera_to_preview_matrix.postscale(mcamerasurface.getview().getwidth() / 2000f, mcamerasurface.getview().getheight() / 2000f);
camera_to_preview_matrix.posttranslate(mcamerasurface.getview().getwidth() / 2f, mcamerasurface.getview().getheight() / 2f);
}
camera api坐标系转换到camera api2坐标系
private rect convertrecttocamera2(rect crop_rect, rect rect) {
// cameracontroller.area is always [-1000, -1000] to [1000, 1000] for the viewable region
// but for cameracontroller2, we must convert to be relative to the crop region
double left_f = (rect.left 1000)/2000.0;
double top_f = (rect.top 1000)/2000.0;
double right_f = (rect.right 1000)/2000.0;
double bottom_f = (rect.bottom 1000)/2000.0;
int left = (int)(crop_rect.left left_f * (crop_rect.width()-1));
int right = (int)(crop_rect.left right_f * (crop_rect.width()-1));
int top = (int)(crop_rect.top top_f * (crop_rect.height()-1));
int bottom = (int)(crop_rect.top bottom_f * (crop_rect.height()-1));
left = math.max(left, crop_rect.left);
right = math.max(right, crop_rect.left);
top = math.max(top, crop_rect.top);
bottom = math.max(bottom, crop_rect.top);
left = math.min(left, crop_rect.right);
right = math.min(right, crop_rect.right);
top = math.min(top, crop_rect.bottom);
bottom = math.min(bottom, crop_rect.bottom);
log.i(tag, "[touch aeaf] convertrecttocamera2 crop_rect:" crop_rect
", rect:" rect
", result:" new rect(left, top, right, bottom));
return new rect(left, top, right, bottom);
}
view坐标转换到camera api2坐标
/**
* given (nx, ny) \in [0, 1]^2, in the display's portrait coordinate system,
* returns normalized sensor coordinates \in [0, 1]^2 depending on how the
* sensor's orientation \in {0, 90, 180, 270}.
*
* returns null if sensororientation is not one of the above.
*
*/
public static pointf normalizedsensorcoordsfornormalizeddisplaycoords(
float nx, float ny, int sensororientation) {
switch (sensororientation) {
case 0:
return new pointf(nx, ny);
case 90:
return new pointf(ny, 1.0f - nx);
case 180:
return new pointf(1.0f - nx, 1.0f - ny);
case 270:
return new pointf(1.0f - ny, nx);
default:
return null;
}
}
/** compute 3a regions for a sensor-referenced touch coordinate.
* returns a meteringrectangle[] with length 1.
*
* @param nx x coordinate of the touch point, in normalized portrait coordinates.
* @param ny y coordinate of the touch point, in normalized portrait coordinates.
* @param fraction fraction in [0,1]. multiplied by min(cropregion.width(), cropregion.height())
* to determine the side length of the square meteringrectangle.
* @param cropregion crop region of the image.
* @param sensororientation sensor orientation as defined by
* cameracharacteristics.get(cameracharacteristics.sensor_orientation).
*/
private static meteringrectangle[] regionsfornormalizedcoord(float nx, float ny,
float fraction, final rect cropregion, int sensororientation) {
// compute half side length in pixels.
int mincropedge = math.min(cropregion.width(), cropregion.height());
int halfsidelength = (int) (0.5f * fraction * mincropedge);
// compute the output meteringrectangle in sensor space.
// nx, ny is normalized to the screen.
// crop region itself is specified in sensor coordinates.
// normalized coordinates, now rotated into sensor space.
pointf nsc = camerautil.normalizedsensorcoordsfornormalizeddisplaycoords(
nx, ny, sensororientation);
int xcentersensor = (int)(cropregion.left nsc.x * cropregion.width());
int ycentersensor = (int)(cropregion.top nsc.y * cropregion.height());
rect meteringregion = new rect(xcentersensor - halfsidelength,
ycentersensor - halfsidelength,
xcentersensor halfsidelength,
ycentersensor halfsidelength);
// clamp meteringregion to cropregion.
meteringregion.left = camerautil.clamp(meteringregion.left, cropregion.left, cropregion.right);
meteringregion.top = camerautil.clamp(meteringregion.top, cropregion.top, cropregion.bottom);
meteringregion.right = camerautil.clamp(meteringregion.right, cropregion.left, cropregion.right);
meteringregion.bottom = camerautil.clamp(meteringregion.bottom, cropregion.top, cropregion.bottom);
return new meteringrectangle[]{new meteringrectangle(meteringregion, camera2_region_weight)};
}